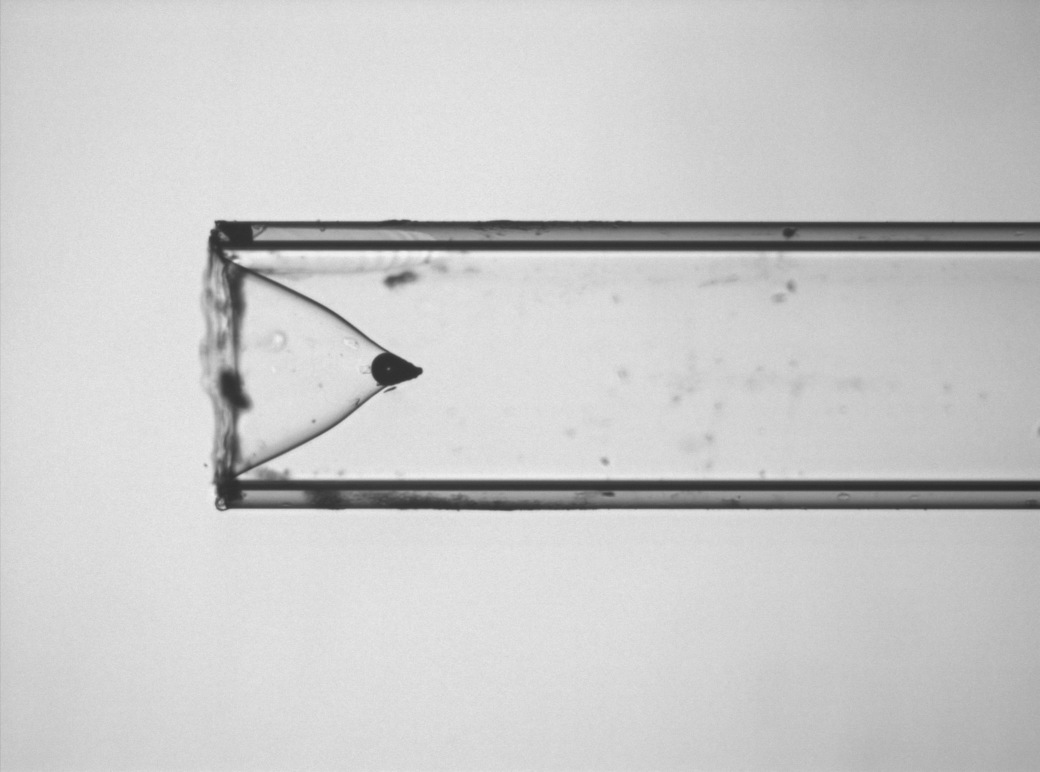
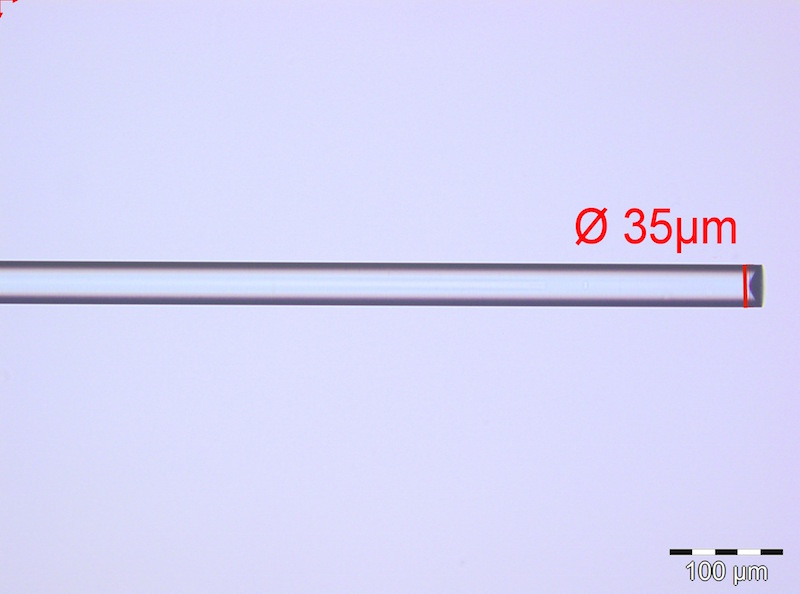
Optical fiber processing for shaping and joining of optical fibers
At Fraunhofer IZM, a wide variety of fiber optic components have been developed in order to cover the current demand in areas of Telecom, Datacom, Medicine and High-power Lasing.
Optical fibers with different geometries and spectral operation from UV to MIR can be processed to create radial-firing fibers, fused couplers, lensed fibers, bundles, fiber caps, 3D resonators, bended fibers, connections of fiber-to-chip & fiber-to-GRIN lens, etc. Customized CO2 laser processing systems, IR heaters, Vytran cleaver and Fujikura splicer are used as standard tools.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM
Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM