Ultrafine pitch soldering on flexible substrates
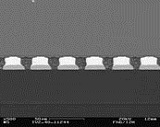
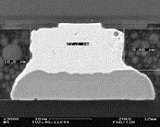

Interconnection pitches tend to be tight and bump sizes are decreasing. Using high precise flip chip bonding machines, IC’s with pitches down to 40µm are soldered onto flexible substrates. The substrates are fixed by vacuum or product-specific mechanical fixtures. Interconnection metallurgies such as AuSn with a small eutectic solder volume during the melting process avoid solder bridging and benefit from fluxless soldering. The bumping of AuSn can be performed on wafer level. Alternatively electroplated, as well as single chip stud bumped Au bumps, can be soldered onto substrates with a Sn surface metallization.
Due to the high thermal load during the bonding process, polyimide substrates with adhesiveless metallization are preferably used.
An underfilling of small gaps between chip and substrate will increase the reliability of the package. Underfiller materials with tiny filler particles meet the flow requirements in gaps of 20µm or less.
In addition to the thermode bonding process, the adhesive joining technology using ACA/ACF is an alternative for ultrafine pitch assemblies. Driver IC’s for e-ink displays are mounted onto thin film substrates. Due to the requirements of Au bumps on the chip and thin Au metallisation on the substrate tracks, an adhesive bonding technology using an ACF has been chosen.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM
Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM