Reliability evaluation with FEM
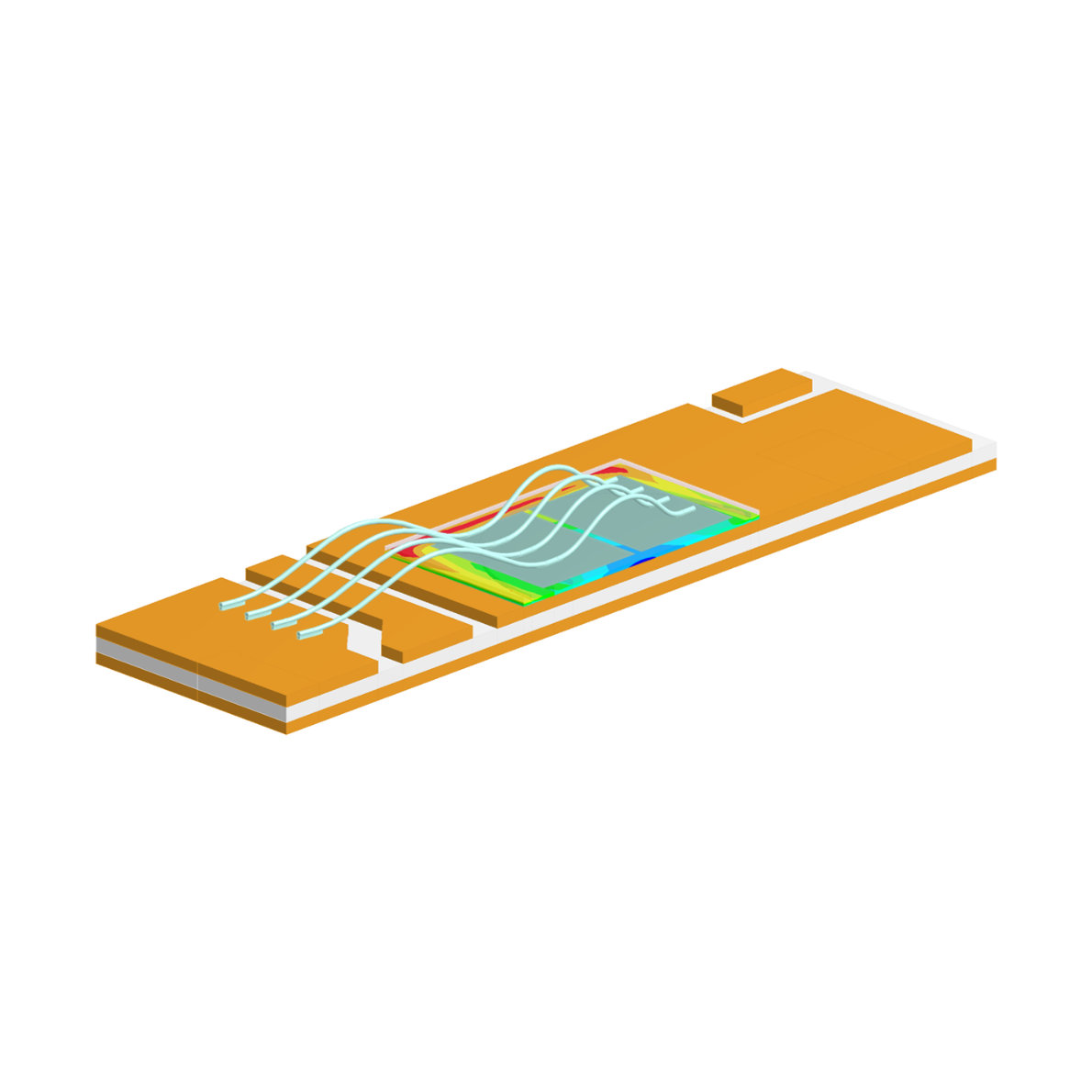
To identify weak points in the early stages of development, or to obtain the optimum geometry under consideration of external loads, finite element simulation (FE) are applied. By means of so-called multiphysics simulations, e.g. thermo-mechanical, electro-thermal, and electro-mechanical couplings can be considered. In addition, moisture diffusion and swelling can be calculated. Applying material failure models allows the evaluation of stress limits and or an estimation of the expected lifetime
Reliability evaluation with FEM concentrate on:
- Realization of geometry: Based on CAD data, cross-sectional images or as part of the process and technology development
- Materials data selection: good material data is a key element for reliability assessment. For many materials, data is already available. For new materials or extended fields of application (e.g. high temperature), additional material properties can be characterized and prepared for the numerical simulations
- Processing simulations: By simulating assembly and process steps, the loads that occur can be evaluated. Typical evaluation criteria are, for example, maximum permissible thermo-mechanical deformation (warpage) and fracture stress.
- Thermal management: Virtual design of the thermal concept for reliable heat dissipation, by taking into account the operating conditions (static / transient, ambient conditions, cooling boundary conditions).
- Sensitivity analysis: Complex relationships between design parameters (e.g. geometric variables, material data, etc.) and external loads can be made graphically visible by means of sensitivity analyses. This enables an optimal system design.
- Lifetime calculation: Lifetime models exist for many frequently occurring failure mechanisms. The simulation results (e.g. damage parameters) can be converted into an expected lifetime. Examples include thermo-mechanical fatigue of solder joints, Al thick wire bonds and vias and electro-migration. The development of new lifetime models is also part of our research.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM
Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Microintegration IZM